Yangtze Delta
The Yangtze (Chang Jiang) is the longest river in China and the third longest river in the world, with a length of 3,900 mi (6,276 km). The river originates in the Tanggula Mountains of Qinghai Province, about 16,000 ft (4,880 m) above sea level. It follows an irregular course as it flows from west to east through the provinces of Qinghai, Tibet, Sichuan, Yunnan, Hubei, Hunan, Jiangxi, Anhui, and Jiangsu. The world’s largest dam, the Three Gorges, is located on the Yangtze in Hubei Province.
The river enters the East China Sea where the basin drains an area of approximately 700,000 mi2 (1,800,000 km2). The discharge carries a load of silt that is estimated to be about 22,000 m3/s at the river’s mouth. Although subsidence is taking place in the delta, deposition is occurring at a more rapid rate.
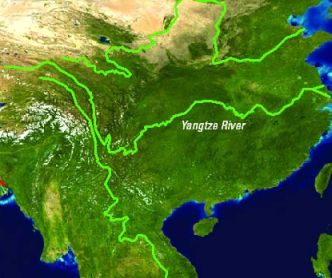
Source: U.S. Geological Survey
General characteristics
- Continent: Asia
- Location: 31°44’N, 121°52’E
- Basin of deposition: East China Sea
- Delta area (km2): 66669
- Number of river mouths: 3
- Spring Tide (m): 3.66
- Major Cities: Shanghai
- Basin area (10^3 km2): 1354.2
- River length (km): 3807
- Average rainfall (mm/y) : 1190
- Maximum rainfall (mm/y) : 1917
- Minimum rainfall (mm/y): 572
- Annual average discharge (m3/s): 2511
- Maximum discharge (m3/s): 473
- Minimum discharge (m3/s): 9261